B12 Injections: Benefits, Risks, and Who Should Consider Them
Vitamin B12 plays a crucial role in maintaining your body’s health. It supports red blood cell formation, DNA synthesis, and neurological function. A deficiency in vitamin B12 can lead to serious health issues, including fatigue, cognitive difficulties, and nerve damage.
B12 injections provide a direct method to deliver this essential nutrient into your bloodstream, bypassing the digestive system. This is particularly important for individuals who struggle to absorb vitamin B12 from food or oral supplements.
This article explores B12 Injections: Benefits, Risks, and Who Should Consider Them. You will learn about:
- The advantages of using B12 injections for correcting deficiencies
- Potential risks associated with the treatment
- Which groups of people are most likely to benefit from injections
Understanding these factors helps you make informed decisions about managing vitamin B12 deficiency effectively.
For those considering B12 injections as a solution to their deficiencies, it’s essential to source these injections from reputable providers. Online pharmacies like MisterPharmacist in Toronto offer fast prescription delivery services, making it easier for individuals to obtain their necessary medications. However, when selecting an online pharmacy, it’s crucial to understand what makes an online pharmacy the best in Toronto. This knowledge will help you make informed choices when purchasing medications online.
Understanding Vitamin B12 and Its Role in the Body
Vitamin B12 plays a crucial role in maintaining several vital functions within the body. Its primary functions include:
- Red blood cell production: Vitamin B12 is essential for the formation and maturation of red blood cells. Without adequate B12, red blood cells can become large and abnormal, leading to a form of anemia known as megaloblastic anemia.
- DNA synthesis: This vitamin is necessary for proper DNA replication, supporting cell division and growth throughout the body.
- Neurological health: Vitamin B12 contributes to maintaining the myelin sheath that protects nerve fibers. Deficiency can result in neurological symptoms such as numbness, tingling, memory problems, and difficulty walking.
Several factors contribute to vitamin B12 deficiency. The condition is relatively common, affecting certain populations more than others:
- Absorption issues: Conditions like atrophic gastritis, Crohn’s disease, celiac disease, or surgeries that reduce stomach acid or intrinsic factor production can impair B12 absorption.
- Dietary insufficiency: Vegans and vegetarians who do not consume animal products may lack sufficient vitamin B12 intake since it is naturally found in meat, fish, eggs, and dairy.
- Age-related decline: Older adults often experience reduced stomach acid production, which hinders the release of vitamin B12 from food sources.
- Medications: Some drugs interfere with vitamin B12 absorption or metabolism.
Identifying risk factors for deficiency is important because untreated low levels can lead to serious hematologic and neurological complications.
What Are B12 Injections and How Are They Administered?
Definition of B12 Injections
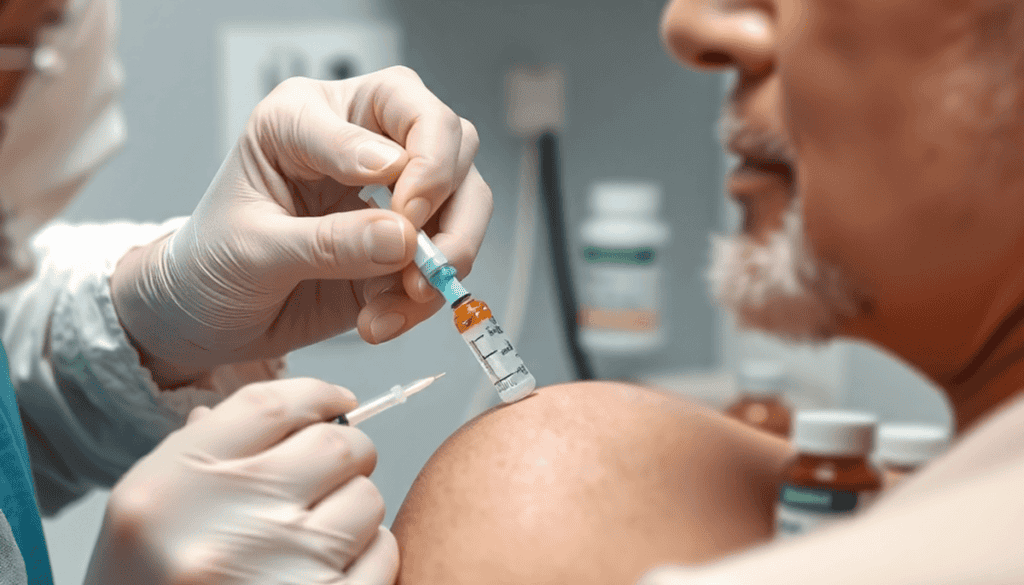
B12 injection definition refers to a medical treatment where vitamin B12 is delivered directly into the body through an injection. These injections typically contain cyanocobalamin or hydroxocobalamin, synthetic forms of vitamin B12 used to quickly increase blood levels of the vitamin.
How B12 Injections Are Given
The primary administration method for B12 injections is intramuscular injection, meaning the shot is given deep into a muscle, usually in the upper arm or thigh. This allows for rapid absorption into the bloodstream. A healthcare professional typically administers the injection, although some patients may be trained to self-administer under medical supervision.
Differences Between B12 Injections and Oral Supplements
Differences between B12 injections and oral supplements include:
- Absorption: Injections bypass the digestive system entirely, delivering vitamin B12 directly to the bloodstream. Oral supplements must pass through the stomach and intestines, where absorption can be limited by factors like low stomach acid or lack of intrinsic factor.
- Speed of effect: Injections raise vitamin B12 levels more quickly than oral supplements, making them useful in cases of severe deficiency or when immediate replenishment is needed.
- Usage scenarios: Oral supplements work well for many individuals with mild deficiency or adequate absorption capacity. Injections are preferred when absorption issues are present due to medical conditions or surgeries affecting the gastrointestinal tract.
Understanding this distinction helps you identify which form of supplementation might be appropriate based on your health status and needs.
Benefits of B12 Injections: Who Can Benefit from This Treatment?
Vitamin B12 injections offer a direct and efficient method for rapidly raising blood vitamin levels. This is crucial when immediate correction of deficiency is needed. The injections bypass the digestive system, delivering vitamin B12 straight into the bloodstream, ensuring quick absorption and utilization by the body.
Who Can Benefit from B12 Injections?
People experiencing symptoms related to vitamin B12 deficiency often find relief through these injections. Common symptoms that respond well include:
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness that doesn’t improve with rest
- Neurological issues: Numbness, tingling sensations, and balance problems
- Memory difficulties: Trouble concentrating or recalling information
- Mood disturbances: Depression, irritability, and mood swings
- Dizziness: Lightheadedness or feeling faint
Untreated deficiency can escalate to serious health problems such as pernicious anemia—a condition where red blood cell production is impaired—and irreversible neurological damage. B12 injections help prevent these complications by restoring adequate levels promptly.
Conditions That May Require B12 Injections
Individuals with absorption difficulties benefit most from injections. Conditions like Crohn’s disease, celiac disease, or previous gastrointestinal surgeries can impair the gut’s ability to absorb oral supplements effectively. In such cases, B12 injections provide a reliable alternative to maintain sufficient vitamin levels and avoid long-term health consequences.
However, it’s important to note that some symptoms associated with vitamin B12 deficiency may overlap with other serious conditions. For instance, syphilis, which is currently experiencing a resurgence, can present with fatigue and neurological issues among its symptoms. Early detection and treatment are vital in such cases.
Additionally, if you’re experiencing persistent fatigue along with urinary symptoms, it could be indicative of a bladder infection, which is another condition that requires immediate medical attention.
Furthermore, certain measles symptoms may also mimic those of a B12 deficiency. It’s essential to consult healthcare professionals for accurate diagnosis and treatment tailored to your specific health needs.
Who Should Consider B12 Injections?
Identifying the right candidates for B12 injections is crucial for effective treatment. These injections are primarily recommended for individuals diagnosed with vitamin B12 deficiency who experience absorption issues and cannot effectively increase their levels through oral supplements.
Certain high-risk groups naturally benefit from this form of supplementation:
- Older adults over 60 face a higher risk of deficiency due to reduced stomach acid production, which impairs vitamin B12 absorption.
- Vegetarians and vegans often lack sufficient intake of animal-based foods, the primary natural sources of B12, making injections a useful option when dietary adjustments or oral supplements fall short.
- Patients with gastrointestinal disorders such as Crohn’s disease or celiac disease frequently struggle with nutrient absorption, necessitating direct vitamin delivery through injections.
- Individuals who have undergone gastrointestinal or weight loss surgeries may lose intrinsic factor or stomach acid essential for B12 absorption, making injections necessary to maintain adequate levels. For families navigating such medical situations, it’s important to know how to manage other aspects of health, such as redosing after vomiting, which can complicate the administration of any medication including B12.
- Those diagnosed with pernicious anemia require ongoing supplementation since their bodies cannot produce intrinsic factor, a protein vital for vitamin B12 uptake.
- People managing chronic conditions that impact absorption often depend on regular B12 injections to prevent deficiency-related complications.
This targeted approach ensures that those truly in need receive the most efficient form of supplementation while avoiding unnecessary treatments for others.
Oral Supplements vs. B12 Injections: Which Is More Effective?
When evaluating oral vs injection B12 supplements, understanding their differences in efficacy is essential. Oral supplementation offers a convenient and non-invasive method to maintain adequate vitamin B12 levels for many people. Tablets, capsules, or sublingual forms can effectively raise B12 in individuals with normal digestive function.
Scientific studies support the efficacy of oral supplements in treating mild to moderate deficiencies. High-dose oral B12 (usually 1000–2000 mcg daily) can bypass some absorption limitations through passive diffusion, making it a viable option for many patients. This method eliminates the discomfort and inconvenience associated with injections.
Situations favoring injections arise primarily when absorption is severely impaired:
- Pernicious anemia patients lack intrinsic factor, which is critical for oral B12 absorption.
- Gastrointestinal disorders like Crohn’s disease or celiac disease disrupt nutrient uptake.
- Post-surgical conditions such as gastric bypass reduce stomach acid and intrinsic factor production.
- Severe deficiency symptoms requiring rapid correction.
In these cases, intramuscular B12 injections provide a direct route into the bloodstream, ensuring immediate availability and therapeutic effect. The injection bypasses the gastrointestinal tract, making it indispensable for those who cannot reliably absorb oral supplements.
Choosing between oral and injectable forms depends on individual diagnosis, severity of deficiency, and underlying absorption capacity. Consulting a healthcare provider helps determine the most appropriate approach based on your specific needs.
Common Myths and Misconceptions About B12 Injections
Vitamin B12 injections often attract various misunderstandings that can lead to misuse or unrealistic expectations. These B12 injection myths are important to clarify, especially for those considering this treatment.
1. Energy Boost Claims
A common misconception is that B12 injections serve as an energy enhancer for people without a deficiency. Scientific research does not support this claim. If your vitamin B12 levels are normal, injections will not provide a noticeable increase in energy or stamina. Energy improvements typically come from correcting an actual deficiency rather than supplementation beyond normal levels.
2. Weight Loss Claims
Another prevalent myth suggests that B12 injections aid weight loss. There is no credible scientific evidence backing this assertion in individuals who are not deficient. Weight loss requires a comprehensive approach including diet, exercise, and lifestyle changes. Relying on B12 injections alone for this purpose is ineffective and unsupported by clinical data.
3. Appropriate Medical Use Only
B12 injections should be reserved for treating confirmed deficiencies or specific medical conditions affecting absorption. Using them without medical indication risks unnecessary procedures and expense. Healthcare providers emphasize proper diagnosis before starting any B12 injection regimen to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Understanding these points helps separate fact from fiction about B12 Injections: Benefits, Risks, and Who Should Consider Them, supporting informed decisions about their use. It’s crucial to remember that while B12 injections can be beneficial, they should always be administered under proper medical guidance to avoid potential risks and complications.
Risks and Side Effects of B12 Injections: What You Need to Know
B12 injections have a generally low risk profile, making them a safe choice for most people when administered correctly. Understanding the risks of B12 injections and possible side effects helps set realistic expectations.
Common, mild side effects include:
- Pain or discomfort at the injection site
- Mild diarrhea
- Itching or rash
These reactions are usually temporary and resolve without intervention.
Severe allergic reactions such as anaphylaxis are rare, but they require immediate medical attention. Very uncommon complications reported include:
- Pulmonary edema (fluid in the lungs)
- Blood clots
These serious side effects occur in exceptional cases and are typically linked to individual sensitivities or underlying health conditions.
Vitamin B12 is water-soluble with a very low toxicity risk. There is no established upper limit for intake since excess amounts are excreted through urine rather than stored in the body. This means concerns about overdose or long-term toxicity from injections are minimal.
Knowing these risks allows you to weigh the safety of B12 injections against their benefits, especially if you belong to groups prone to deficiency or poor absorption.
In some cases, individuals may be prescribed ADHD medications along with B12 supplements due to potential deficiencies caused by certain medications. For those seeking more information on this topic, a detailed comparison of ADHD medications in Canada could provide valuable insights into effectiveness, side effects, and online prescription options available for 2025.
How to Get Tested for Vitamin B12 Deficiency: A Guide to Diagnosis Methods
Proper diagnosis plays a crucial role before starting treatment with B12 injections. Self-diagnosing or assuming deficiency without testing can lead to unnecessary treatments or overlooking other health issues.
Testing for vitamin B12 deficiency typically involves several diagnostic methods, mainly focusing on blood tests:
- Serum Vitamin B12 Test: Measures the level of vitamin B12 circulating in your blood. Low levels often indicate a deficiency.
- Methylmalonic Acid (MMA) Test: Elevated MMA levels suggest functional B12 deficiency, even if serum levels appear normal.
- Homocysteine Test: High homocysteine may also point to insufficient B12, though it can be influenced by other factors like folate levels.
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): Helps identify anemia, which is a common consequence of prolonged B12 deficiency.
You should consult a healthcare provider if you experience symptoms such as persistent fatigue, numbness or tingling in hands and feet, memory problems, or unexplained neurological issues. Individuals with risk factors—like older age, strict vegetarian or vegan diets, gastrointestinal disorders, or history of certain surgeries—should also seek testing proactively.
In some cases, additional testing methods such as testing SD might be recommended to rule out other potential health issues that could be contributing to your symptoms.
Early and accurate diagnosis ensures that treatment plans are tailored specifically to your needs, whether that involves injections or oral supplementation. It’s also worth noting that while addressing a vitamin B12 deficiency, ensuring maximum absorption of other essential nutrients like zinc is equally important. For instance, when taking zinc supplements, it’s advisable to [follow certain dietary dos and don’ts](https://misterpharmacist.com/dietary-dos-and-donts/zinc-maximum-absorption) for optimal absorption.
Final Recommendations on Considering B12 Injections as a Treatment Option
Vitamin B12 injections offer a safe and effective way to address deficiency, especially when rapid elevation of blood levels is needed or when absorption issues prevent oral supplementation from working. Understanding the summary of benefits risks indications helps you make an informed decision.
Who should consider B12 injections:
- Individuals with confirmed vitamin B12 deficiency who cannot absorb oral supplements effectively
- Older adults, particularly over age 60, at higher risk for deficiency
- People with gastrointestinal disorders or surgeries impairing absorption
- Those diagnosed with pernicious anemia or requiring ongoing supplementation
For many others, oral supplements provide a convenient and efficient alternative.
Seeking professional medical advice before starting B12 injections ensures proper diagnosis and tailored treatment. Maintaining adequate vitamin B12 intake is essential, whether through diet rich in animal products or appropriate supplementation based on your individual needs.
B12 injections should be viewed as a targeted therapy rather than a general wellness booster. Appropriate use maximizes benefits while minimizing risks.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What is vitamin B12 and why is it important for the body?
Vitamin B12 is an essential nutrient that plays a critical role in red blood cell production, DNA synthesis, and maintaining neurological health. Deficiency can lead to fatigue, neurological issues, and serious complications like pernicious anemia.
What are B12 injections and how do they differ from oral supplements?
B12 injections are intramuscular shots of vitamin B12 designed to rapidly increase blood levels of the vitamin. Unlike oral supplements, injections bypass the digestive system, making them effective for individuals with absorption difficulties.
Who should consider receiving B12 injections?
Individuals diagnosed with vitamin B12 deficiency who have trouble absorbing oral supplements, older adults over 60, vegetarians and vegans lacking sufficient animal-based intake, patients with gastrointestinal disorders or surgeries affecting absorption, and those with pernicious anemia or chronic conditions requiring ongoing supplementation should consider B12 injections.
Are B12 injections effective for boosting energy or aiding weight loss in people without deficiency?
No scientific evidence supports claims that B12 injections boost energy or promote weight loss in individuals without a deficiency. These injections should be used appropriately under medical guidance for treating confirmed deficiencies.
What are the potential risks and side effects of B12 injections?
B12 injections generally have a low risk profile. Mild side effects may include pain at the injection site, diarrhea, or itching. Rarely, allergic reactions such as anaphylaxis or very uncommon complications like pulmonary edema or blood clots can occur. There is no known toxicity concern due to the vitamin’s low toxicity risk.
How can one get tested for vitamin B12 deficiency before considering injections?
Proper diagnosis involves consulting a healthcare provider who may order blood serum level tests to detect deficiency. Testing ensures appropriate treatment decisions between oral supplements and injections based on individual needs.